Publicity: 2022
Collection of News Articles or Videos Relating to E3SM
NCAR|CGDINCITE 2023 Awards:
E3SM’s Mark Taylor from Sandia National Laboratory received 450,000 node-hours on Summit and 1,250,000 node-hours on Frontier to model the earth’s climatic systems.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science announced allocations of supercomputer access to 56 high-impact computational science projects for 2023 through its Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program. These awards, which will pursue transformational advances in science and engineering, account for 60 percent of the available time on the leadership-class supercomputers at DOE’s Argonne and Oak Ridge National Laboratories.
Additional link to INCITE 2023 Awards:
Argonne researcher to participate in incite project: Mark Taylor (see page 15)
NCAR|CGD:
CATALYST performs foundational coordinated research in a team oriented, collaborative environment. It aims to advance a robust understanding of the modes of Earth system variability and change by utilizing the DOE Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM), the NCAR Community Earth System Model (CESM), Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP) multi-model data sets, a hierarchy of simpler models, machine learning methods, and numerous observational data sets.
Eos:
Are We Entering The Golden Age Of Climate Modeling?
Thanks to the advent of exascale computing, local climate forecasts may soon be a reality. And they’re not just for scientists anymore.
ESiWACE:
ESiWACE2 2nd Virtual Workshop on Emerging Technologies successfully completed
The second session on programming models and hardware interplay chaired by Andrew Porter (STFC) addressed the use of domain specific languages (DSLs) for climate and earth system modelling, experiences with the C++ library Kokkos in the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) and DestinE: opportunities & challenges for digital twins of the Earth System.
UNM Newsroom:
DOE awards $3.3 million to UNM professor, research on climate prediction
An unpredictable picture of a future fueled by climate change is getting clearer with the help of The University of New Mexico and Department of Energy (DOE).
Department of Mathematics & Statistics Professor Emerita Deborah Sulsky has just been awarded a $3.3 million grant as part of the DOE’s efforts to improve its Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM).
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory:
The Science of Hurricanes: Preparing for and Enduring Big Storms
PNNL’s work doesn’t stop at the here-and-now. Researchers are working to better understand how hurricanes and their impacts might be affected by climate change. Ruby Leung, a PNNL atmospheric scientist and Battelle Fellow, is also the chief scientist of the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (better known as E3SM), an Earth system model developed to support DOE’s energy mission.

The meteorological observations made by ARM’s Mobile Research Facility will help produce more accurate rainfall prediction models. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory/Scott Collis
October 12, 2022
PHYS ORG:
New tool helps researchers investigate clouds, rain and climate change
Using an approach developed for NASA, Argonne scientists plan to use EMC2 in collaboration with DOE’s Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM), a high-resolution model designed to examine the most detailed dynamics of climate-generating behavior.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory:
Taking it to the streets: ORNL models climate solutions for U.S. cities
“We have a lot of experience with what’s known as the ModEx approach — integrating environmental observations from widespread networks into large-scale models,” Ricciuto said. “ORNL is continually refining and calibrating such models, and we look forward to incorporating new knowledge about urban ecosystems into E3SM through this project.” By pinpointing climate impacts and mitigation for specific underserved neighborhoods, the Urban IFL brings a new granularity to ORNL’s modeling, he added.
ATMO@UH:
Webinar Presented by Dr. Shaocheng Xie of LLNL at the School of Ocean and Earth Science Technology (SOEST) at the University of Hawai’i at Manoa
ITPro.:
Climate supercomputer model to receive $70 million research boost
The US Department of Energy (DoE) has announced seven new projects to receive a total of $70 million funding, which will work to improve its climate prediction model.
The Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) is the DoE’s advanced model for climate prediction, operating at exascale levels to provide extremely detailed simulations of weather systems, changes in ocean currents, and decade-long shifts in climate.
insideHPC:
Los Alamos, PNNL, Univ. of New Mexico Researchers to Lead $70M DOE HPC Climate Model Projects
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $70 million in funding for seven projects intended to improve climate prediction and aid in the fight against climate change. The research will be used to accelerate development of DOE’s Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM), enabling scientific discovery through collaborations between climate scientists, computer scientists and applied mathematicians.
University of Washington | Bothell:
Expanding regional research opportunities
Programming predictions:
Also part of the 2022 REU cohort is Colton Maybee, an HU junior majoring in Computer Science. He spent the summer at the Pacific Northwest National Lab researching an efficient way to detect solution reproducibility in earth system models.
“An earth system model is an open-source software for building climate, weather prediction, data assimilation and other earth science software applications,” Maybee explained. “The model simulates all relevant aspects of the earth system including the atmosphere, land, ocean, ice and sea ice.”
HPCWire:
DOE and ORNL Dedicate Frontier Supercomputer
The supercomputer, which in May became the first system to achieve over 1.0 exaflops of 64-bit performance on the HPL benchmark, which determines system rankings on the prestigious, semi-annual Top500 list. The unveiling was a crowning achievement for ORNL and the U.S. Department of Energy.
“As a scientist who has been working in climate change for pretty much my whole career, I’m particularly excited to see how the Energy Exascale Earth System Model will be able to transform our understanding of several key earth system processes, and in particular, help us understand our changing climate with the urgency that’s needed,” said Berhe.
EESM:
Overall Performance Measures
3rd Quarter Metric Completed:
Demonstrate that Antarctic and Southern Ocean Regionally Refined Mesh (rrm) Improves Fully Coupled E3SM Simulations of Antarctic Sub-Ice-Shelf Melt Fluxes and Southern Ocean Climate
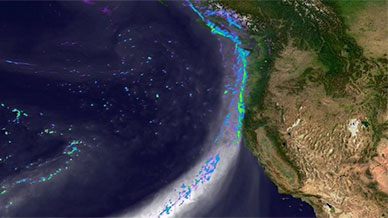
Snapshot of the simulated landfall of an atmospheric river along the west coast of North America on February 11, 2020. Grey tones depict water vapor. Colors indicate precipitation intensity from blue (light rain) to green (very strong precipitation). Credit: Department of Energy Office of Science, Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) project.
August 9, 2022
SciTechDaily:
Science Made Simple: What are Atmospheric Rivers?
Atmospheric rivers are a very important part of the Earth’s climate. They are responsible for 90% of the movement of moisture from the tropics toward the poles. This means atmospheric rivers are a major factor in the formation of clouds and therefore have a significant influence on air temperatures, sea ice, and other components of the climate.
Los Alamos National Laboratory:
Collaborative Climate Modeling
Powerful new tools help predict climate change and its potential impacts on national security.
Humans are now living in the warmest climate in modern history. Wildfires, droughts, hurricanes, flooding, extreme heat, and coastal erosion are more intense and more frequent with each passing year.
What do these climate changes mean for national security?

Black carbon, or soot, from wildfires, transportation and other sources has a big impact on global warming, but a data gap has prevented climate-change models from accurately representing that influence. New work by Los Alamos National Laboratory closes the gap with a simple parameter for climate models. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory.
July 22, 2022
Technology Networks Applied Sciences:
Estimates of Soot’s Role in Climate Change Improved by Wildfire-Smoke Observations
New research refining the amount of sunlight absorbed by black carbon in smoke from wildfires will help clear up a longtime weak spot in Earth system models, enabling more accurate forecasting of global climate change.

Black carbon, or soot, from wildfires, transportation and other sources has a major impact on global warming, but a data gap has prevented climate change models from accurately reflecting that impact. New work from Los Alamos National Laboratory closes the gap with a simple climate modeling parameter. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory
July 22, 2022
WHATSNEW2DAY:
Wildfire-smoke observations fill gap in estimating soot’s role in climate change
“Black carbon or soot is the second most potent climate warming agent after CO2 and methane, despite a short lifespan of weeks, but its impact in climate models is still very uncertain,” said James Lee, climate researcher at Los Alamos National Laboratory and corresponding author of the new study in Geophysical Survey Letters on light absorption by wildfire smoke. “Our research will remove that uncertainty.”

Researchers have developed a multiscale modeling framework to refine cloud representation in E3SM climate simulations on GPU-accelerated supercomputers
July 5, 2022
Oak Ridge National Laboratory Leadership Computing Facility:
ECP Advances the Science of Atmospheric Convection Modeling
Researchers supported by the US Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Exascale Computing Project (ECP) have integrated the promising super-parameterization technique for modeling moist convection into the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM). This method enables E3SM to significantly improve cloud resolution while also reducing compute time and cost.
NGEE-Tropics:
Next Generation Ecosystem Experiments
Tree Crown Damage Alters Canopy Structure and Competitive Dynamics
A multi-institutional team of scientists introduce a crown damage module into the Functionally Assembled Terrestrial Ecosystem Simulator (FATES), a submodel of the DOE’s Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM). Using this new functionality, scientists were able to test how crown damage alters forest dynamics relative to equivalent increases in tree mortality.
News from ISSE:
Spring Magazine 2022
Institute for Secure & Sustainable Environment
Climate change is one of the most critical challenges faced by human being and our planet. Researchers at ISSE, closely working with the Climate Change Science Institute at Oak Ridge National Lab (ORNL), is advancing our understanding of climate change and its impacts on human and natural systems. We use Earth system modeling, integrated ground and remote sensing observations, and advanced data analytical tools to study climate change and its impacts on water availability, soil moisture, wildfires, and vegetation. The team is Drs. Yaoping Wang, Yulong Zhang, Jiafu Mao (Joint Professor at ORNL), Joshua Fu, and Mingzhou Jin.
PHYS ORG:
A cloudless future? The mystery at the heart of climate forecasts
We hear a lot about how climate change will change the land, sea, and ice. But how will it affect clouds?
“Low clouds could dry up and shrink like the ice sheets,” says Michael Pritchard, professor of Earth System science at UC Irvine. “Or they could thicken and become more reflective.”
These two scenarios would result in very different future climates. And that, Pritchard says, is part of the problem.
ScienceDaily:
A cloudless future? The mystery at the heart of climate forecasts
New computational approaches help researchers include cloud physics in global models, addressing long-standing questions

HPCwire highlights newly published research in the high-performance computing community and related domains.
April 28, 2022
HPCwire:
E3SM Diags, Sunway Supercomputer, AxoNN, Snellius Suprercomputer & More
The E3SM diagnostics package: a python-based diagnostics package for earth system models evaluation
E3SM Diags is an open-source Python software package that was released in 2017 and developed to support the Department of Energy Energy Exascale Earth System 5 Model project. A multi-institutional team of researchers modeled E3SM Diags after the atmospheric model working group diagnostics package from the National Center for Atmospheric Research.
insideHPC:
ExaIO: Access and Manage Storage of Data Efficiently and at Scale on Exascale Systems
As the word exascale implies, the forthcoming generation exascale supercomputer systems will deliver 1018 flop/s of scalable computing capability. All that computing capability will be for naught if the storage hardware and I/O software stack cannot meet the storage needs of applications running at scale—leaving applications either to drown in data when attempting to write to storage or starve while waiting to read data from storage.
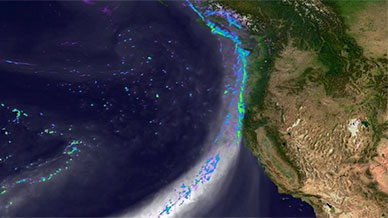
Snapshot of the simulated landfall of an atmospheric river along the west coast of North America on February 11, 2020. Grey tones depict water vapor. Colors indicate precipitation intensity from blue (light rain) to green (very strong precipitation).
April 7, 2022
EurekaAlert!:
Better clouds than ever with new exascale computing-ready atmosphere model
Researchers working on the Energy Exascale Earth System Model (E3SM) project have developed an entirely new global atmosphere model. The model has a resolution 30 times finer than global climate models. This resolution allows scientists to model and study the atmosphere with far more detail than previously possible. A new paper describes the equations that govern the new global atmosphere model and evaluates the model’s first simulation.
Universal Wiser Publisher:
Science Made Simple: What Are Earth System and Climate Models?
Earth system models and climate models are a complex integration of environmental variables used for understanding our planet. Earth system models simulate how chemistry, biology, and physical forces work together. These models are similar to but much more comprehensive than global climate models.
January 20, 2022
ORNL: Updated exascale system for Earth simulations delivers twice the speed
Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s press release story on the E3SM version 2 model release.
“E3SMv2 delivered twice the performance over E3SMv1 when using identical computational resources”
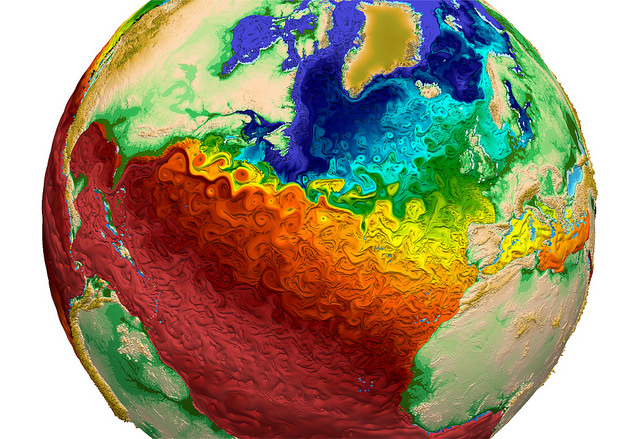
Earth system models like E3SM take advantage of powerful new computers to simulate variations in Earth systems and anticipate changes that will critically impact the U.S. energy sector in coming years.
January 6, 2022
ANL: Updated exascale system for Earth simulations
Argonne National Laboratory’s press release story on the E3SM version 2 model release.
January 7, 2022
HPCwire: Updated Exascale System for Earth Simulations Is Twice as Fast as Predecessor
The high performance computing magazine, HPCwire, featured this story on E3SM in their magazine.
January 7, 2022